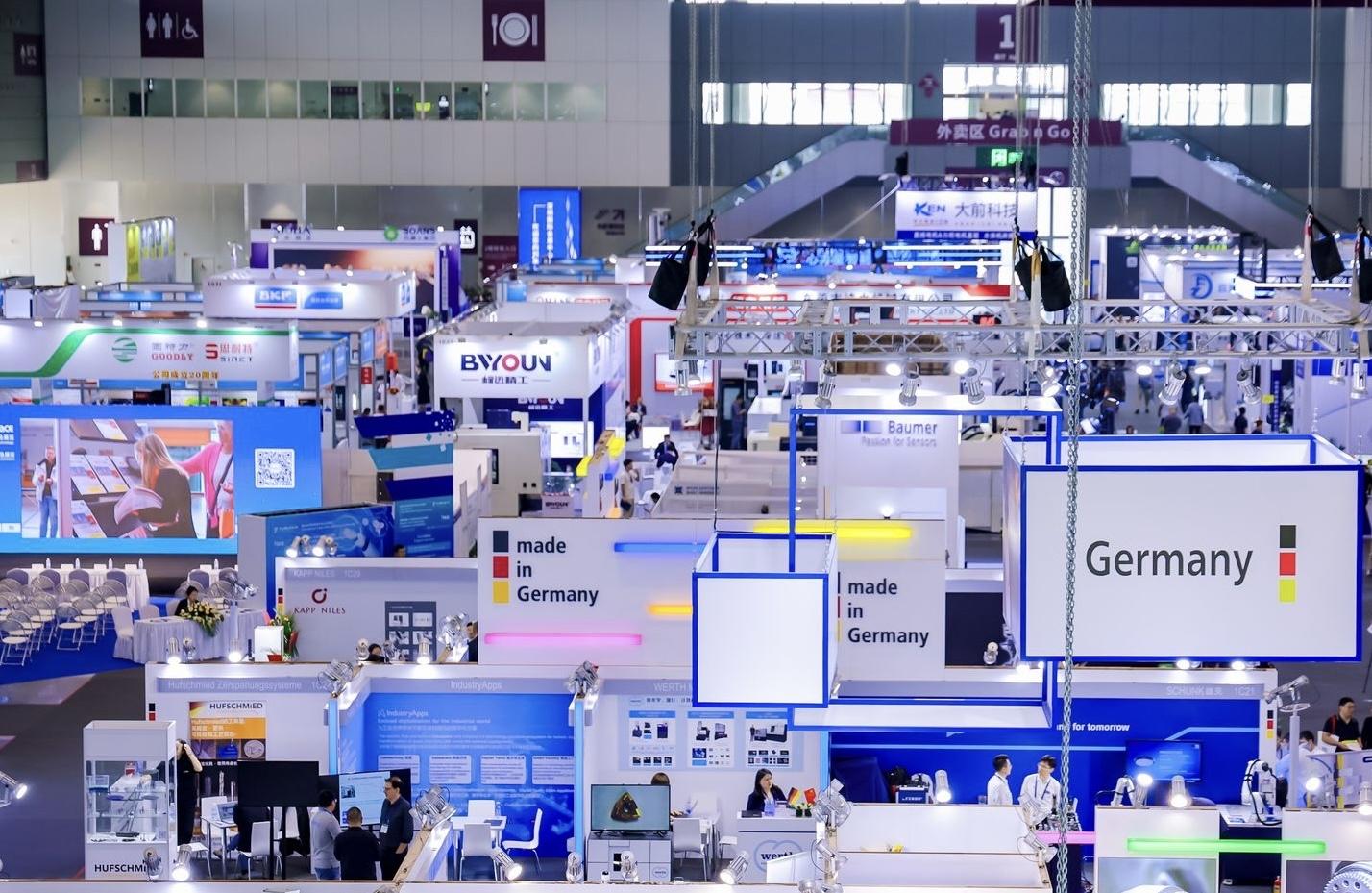
On November 25th, the "China's Regional Innovation Capacity Evaluation Report of 2023" (here in after referred to as the report) was released in Beijing, with Guangdong leading the nation for the 7th consecutive year.

According to the report, in 2023, Guangdong performed well in all dimensions, ranking first in the country in three indicators, including enterprise innovation, innovation performance, and knowledge acquisition, while its indicators of knowledge creation and innovation environment ranked second.
Guangdong's innovation capability can be attributed to the following major factors:
First, Guangdong has a strong economic foundation and economic structure optimized by policies. Enterprises are the main force of innovation, and innovation is the ultimate result of collaboration between brave entrepreneurs and innovative scientific talents. Guangdong leads in various economic indicators nationwide. For example, Guangdong's major industrial enterprises ranked 1st in revenue. In recent years, Guangdong has optimized its industrial structure and enhanced the number and strength of large-scale industrial enterprises and innovative enterprises through policy incentives and guidance. The report shows that there are 67,000 major industrial enterprises in Guangdong, an increase of 20,000 in five years; there are 69,000 high-tech enterprises, more than double in five years.
Second, Guangdong is actively improving the hardware and software of scientific research infrastructure. In terms of hardware, Guangdong has invested a lot of money in laboratory construction to vigorously promote the construction of colleges and universities, laboratories, and scientific research institutes. Two key national laboratories, Pengcheng Laboratory and Guangzhou Laboratory, have already started operation. In terms of software, Guangdong has strengthened the source supply of industrial technology by investing more than one-third of the special funds for provincial science and technology innovation strategies in basic research.
Third, Guangdong actively promotes collaborative innovation. In terms of industrial collaboration, the Guangdong government has built platforms to promote collaborative innovation among enterprises. In terms of the collaboration among enterprises, universities and research institutes, Guangdong universities and colleges focus on cultivating interdisciplinary, inter-college, and multi-major talents in response to market demand and breaking down professional barriers by actively creating cross-training talent models to enhance the practical abilities of engineering students. This not only provides a large number of innovative and practical talents for Guangdong enterprises, but also enables Guangdong universities and colleges to have a better understanding of the market and be more targeted in research and talent cultivation.
Fourth, Guangdong has strengthened the supply of innovation factors. Scientific and technological innovation depends on the supply of factors like the supply of talents, capital, and data. In terms of talents, Guangdong has actively improved various "recruitment plans" and introduced various talents to promote innovation without regional limitations. A vivid example of Shenzhen's talent introduction is that Yan Ning, a famous scientist, founded the Shenzhen Medical Academy of Research and Translation. In terms of capital supply, on the one hand, Guangdong solves the problem of R&D funds for enterprises through financial innovation; on the other hand, it actively connects with domestic and foreign investors through several financial channels in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area to gain more sources for Guangdong enterprises' innovation.
In summary, Guangdong's innovation capability comes from its strong economic and industrial foundation, increased investment in basic scientific research by Guangdong Province, collaboration between enterprises and between enterprises, colleges and research institutions in Guangdong, and abundant supply of various innovation factors. It can be foreseen that Guangdong will continue to explore and develop new fields in promising industries such as the digital economy, new energy, and life sciences, continuously stimulating new driving forces for high-quality development.
(The author is the co-director and researcher of the Digital Economy and Financial Innovation Research Center at Zhejiang University's International Business School, and a member of the Expert Committee for Communication Economy of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology.)
Source:Yangcheng Evening News
时评|广东创新能力连续七年领跑,底气何来?
11月25日,《中国区域创新能力评价报告2023》(以下简称《报告》)在北京发布,广东7年蝉联第一领跑全国。
《报告》中提及,2023年广东企业创新、创新绩效和知识获取3个指标排名全国第一,知识创造和创新环境指标排名全国第二。各维度指标均有较好表现。
总结广东创新能力的形成,离不开如下几大因素:
其一,广东区域经济底蕴雄厚,政策推动结构优化。创新的主力是企业,创新是企业中有冒险精神的企业家和有创新力的科研人才相互协作的最终产物。广东各方面经济指标居于全国领先地位,比如广东规模以上工业企业营收全国排名第一。近些年来,广东通过政策激励和引导,优化产业结构,增强广东规模化工业企业、创新企业的数量和实力。《报告》显示,广东规模以上工业企业达6.7万家,5年增加2万家;高新技术企业达6.9万家,5年翻了2倍多。
其二,广东积极完善科研基础设施。科研基础设施包括硬件和软件,在硬件方面,广东在实验室建设上投入大量资金,大力推进高等院校、实验室、科研院所的建设,鹏城实验室、广州实验室两大“国之重器”挂牌运作;在软件方面,广东增强产业技术源头供给,将1/3以上的省级科技创新战略专项资金投向基础研究。
其三,广东积极推进协同创新。在产业协同方面,广东政府搭建平台,推动企业进行协同创新;在产学研融合方面,广东高校注重针对市场人才需求培养人才,打破专业壁垒,积极打造跨学科、跨学院、多专业横向交叉培养人才模式,增强工科学生工作实践能力,这既为广东企业输送了大量创新型、实用型人才,也让广东科研院校更加了解市场,在研发和人才培育上更加有的放矢。
其四,广东加强创新要素供给。科技创新同样需要要素供给,比如人才供给、资本供给、数据要素供给等。在人才方面,广东积极完善各类“招才计划”,不限地域引进各类人才推动创新。著名科学家颜宁在深圳创立医学科学院,就是深圳引才的一个生动例子;在资本供给方面,广东一方面以金融创新为企业解决研发资金问题。另一方面又积极利用大湾区几个金融窗口和国内外投资人对接,为广东企业创新获取更多源头活水。
综上,广东创新能力来自于广东雄厚的经济产业底蕴,来自于广东省加大基础科研投入,来自于广东企业之间、企业和科研院校之间的协同,也来自于广东充沛的各类创新要素供给。可以预见,广东将在数字经济、新能源、生命科学等未来产业开辟发展新领域、新赛道,不断激发高质量发展新动能。(作者系浙江大学国际联合商学院数字经济与金融创新研究中心联席主任、研究员,工信部信息通信经济专家委员会委员)
文 | 盘和林
图|DMP大湾区工业博览会主办方供图
翻译|白心怡
责编 | 王瑜瑛
校对 | 张家梁
-
Fu Lei Award Promotes Sino-French Cultural Exchange——2024 Sino-French Cultural Events Highly Anticipated
2023-11-27 21:44:44 -
Guangzhou ranks among China's most livable cities for the sixth time
2023-11-26 22:56:45 -
Foshan hosts inaugural Camping Life Expo
2023-11-25 23:51:05 -
From Macao to Beijing, a 71-day journey by bus
2023-11-25 23:51:18