Indian, July 27th —At the 46th session of the World Heritage Committee in New Delhi (India) , the "Beijing Central Axis: A Building Ensemble Exhibiting the Ideal Order of the Chinese Capital" was approved to be inscribed on the World Heritage List. Also at this session, China's "Badain Jaran Desert - Towers of Sand and Lakes" and "Migratory Bird Sanctuaries along the Coast of Yellow Sea-Bohai Gulf of China (Phase II)" , formally submitted in 2020 and 2022 respectively, were reviewed and approved by the World Heritage Committee, also successfully entering the World Heritage List. This brings the total number of World Heritage sites in China to 59, including 15 natural heritage sites and four cultural and natural heritage sites.
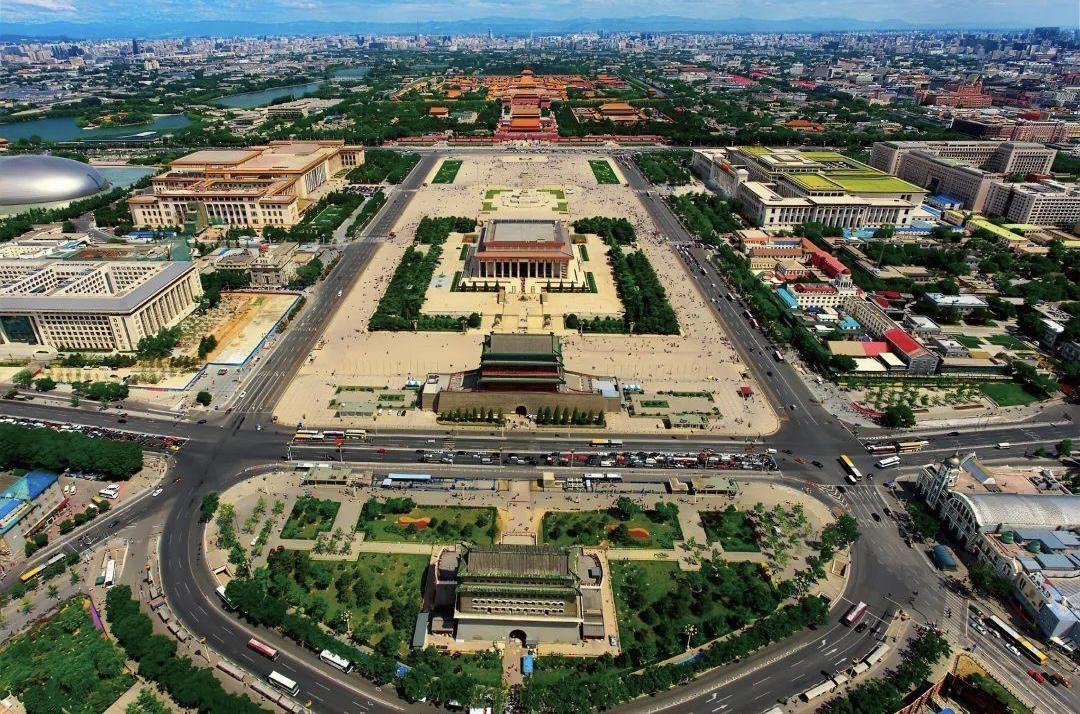

The "Beijing Central Axis" stretches north-south through the old city of Beijing. Built in the 13th century and taking shape in the 16th century, it has evolved and expanded over time to reach 7.8 long, becoming the longest urban axis in the world. The "Beijing Central Axis" is comprised of five major remains: ancient imperial palace gardens, ancient imperial buildings, ancient urban management buildings, national ceremony, and public buildings, and the remains of central roads. Its site selection, layout, cityscape form, and design embody the paradigm of the ideal city described in "The Rites of Zhou: The Records of Trades", demonstrate the Chinese ancient imperial systems and urban planning traditions, and bear witness to the development and evolution of Beijing's city fabric.
It took 12 years for "Beijing Central Axis" to be inscribed on the World Heritage List, a period that can be divided into three stages: the initial stage (2012-2016), the accelerating stage (2017-2021), and the final stage (2022-2024). On May 30th, 2024, the International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS) issued an evaluation report, concluding that the "Beijing Central Axis" should be directly inscribed on the World Heritage List, which provides a solid basis for the inscription.
The Badain Jaran Desert , located on the Alashan Plateau , is an extremely arid temperate desert in northwest China. It is China's third-largest desert and second-largest drifting desert. Its significant landmarks include the tallest stationary dunes on Earth (reaching 460 meters in height), numerous scattered desert lakes, the most extensive area with the singing sand phenomenon, and diverse wind-erosion landforms, which demonstrate extraordinary natural and aesthetic values.
Yang Ziyan, a member of the Chinese delegation to the 46th session of the World Heritage Committee and head of the public relations department of the China Association of National Parks and Scenic Sites , pointed out: "The successful inscription of the 'Badain Jaran Desert' provides a solid foundation for further research into the formation of desert sand dunes and the protection of desert lakes that lie between the dunes. It also fills the gap of desert type for China in World Natural Heritages, which is of great significance. At the same time, it presents to the world the unique value of China's lakes and dune-dominated desert features in terms of natural heritage, demonstrating its universal value as a treasure worthy to be jointly cherished by all mankind."
Source :Yangcheng Evening News
中国两天内新增三处世界遗产
记者获悉,当地时间2024年7月27日,在印度新德里召开的联合国教科文组织第46届世界遗产大会通过决议,将中国申报的“北京中轴线——中国理想都城秩序的杰作”列入《世界遗产名录》。同样在本次世界遗产大会上,我国分别于2020年、2022年正式申报的巴丹吉林沙漠-沙山湖泊群、中国黄(渤)海候鸟栖息地(第二期)顺利通过遗产委员会评审,成功列入《世界遗产名录》。至此,中国世界遗产总数达到59项,包括15项世界自然遗产、4项文化与自然双遗产。
“北京中轴线”纵贯北京老城南北,始建于13世纪,形成于16世纪,此后经不断演进发展,形成今天全长7.8公里、世界上最长的城市轴线。“北京中轴线”由古代皇家宫苑建筑、古代皇家祭祀建筑、古代城市管理设施、国家礼仪和公共建筑以及居中道路遗存等五大类遗存共同组成,其选址、格局、城市形态和设计体现了《周礼·考工记》所记载的理想都城范式,展现了中国古代王朝制度和城市规划传统,见证了北京城市的发展演变。
据悉,北京中轴线申遗历时12年,分申遗启动阶段(2012年至2016年),全面加速阶段(2017年至2021年),攻坚冲刺阶段(2022年至2024年)。2024年5月30日,国际古迹遗址理事会形成评估报告,作出将“北京中轴线”直接列入《世界遗产名录》的最高评估结论,为申遗成功奠定了坚实的专业基础。
巴丹吉林沙漠地处阿拉善高原,属中国西北极干旱的温带荒漠地区,是中国第三大沙漠和第二大流动沙漠。其重要标志包括世界最高的固定沙山(相对高度达 460 米)、最密集的沙漠湖泊、最广阔的鸣沙区域以及多样的风蚀地貌,展现了非凡的自然美学价值。
第46届世界遗产大会中国代表团成员、中国风景名胜区协会遗产外联部主任杨子砚指出:“巴丹吉林沙漠—沙山湖泊群的申遗成功,为进一步研究沙漠沙山的形成和保护沙漠丘间湖泊奠定了基础,也填补了我国在世界自然遗产中没有沙漠类型的这一空白,具有很大意义。同时,在全世界范围内展示了我国湖泊和沙丘沙漠特征在自然遗产方面独一无二的价值,其具有的突出普遍价值是全人类共同呵护的瑰宝。”
文|记者 周欣怡 朱绍杰
译 | 洪婷
-
Poster | The largest renovation in 25 years of the Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hall of Guangzhou has been completed
2024-07-29 21:50:24 -
The 'chill vibe' of China's post-2000s athletes sparks joy on Paris Olympics
2024-07-29 21:42:49 -
A Guangdong teacher's journey to judging at the Olympics
2024-07-29 21:42:49 -
Mutual tourism boom: Chinese travel to Paris for Olympics while French tour China
2024-07-28 23:20:02