The development and application of robots, particularly humanoid robots, are crucial to the evolution of social labor division and human-machine collaboration, making itself a new battleground in technological competition and an emerging track for future industries. During the recently held Guangdong Provincial High-Quality Development Conference, the province emphasized the need to focus efforts on artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics, aiming to establish a new pillar of high-tech, high-growth, and large-scale industries.
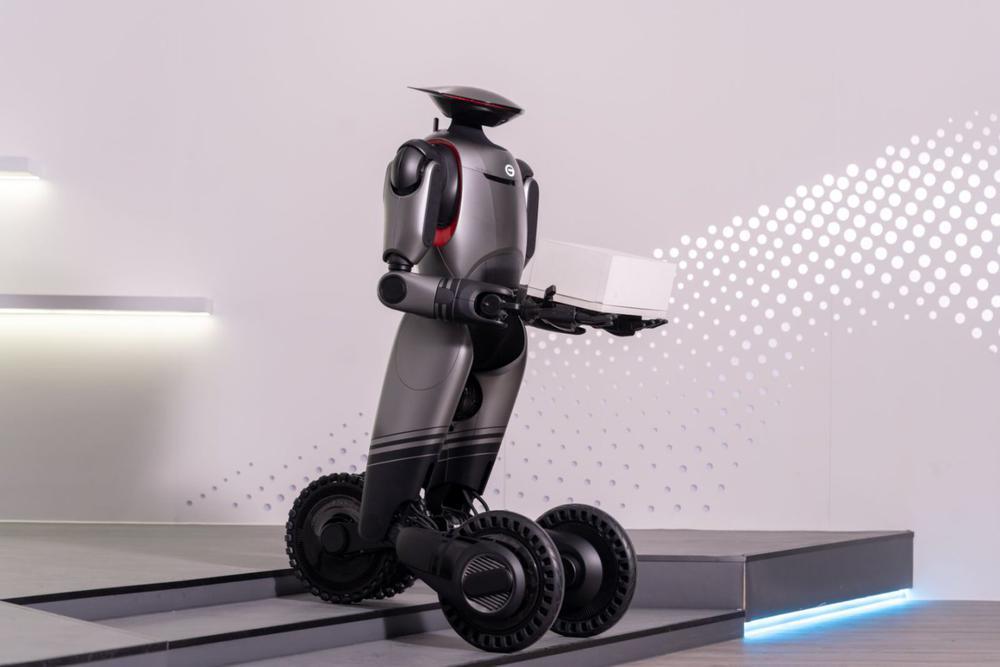

Last year, Guangdong's industrial robot production exceeded 240,000 units (sets), accounting for 44% of the national total, leading the nation for the fifth consecutive year. Guangdong has also established the Embodied AI Robotics Innovation Center of Guangdong Province and the Guangdong Robotics Innovation Center, which have attracted renowned Chinese and international companies, such as KUKA, Han's Laser, MINO, DJI, and UBTECH, while also nurturing a cohort of local "little giants".
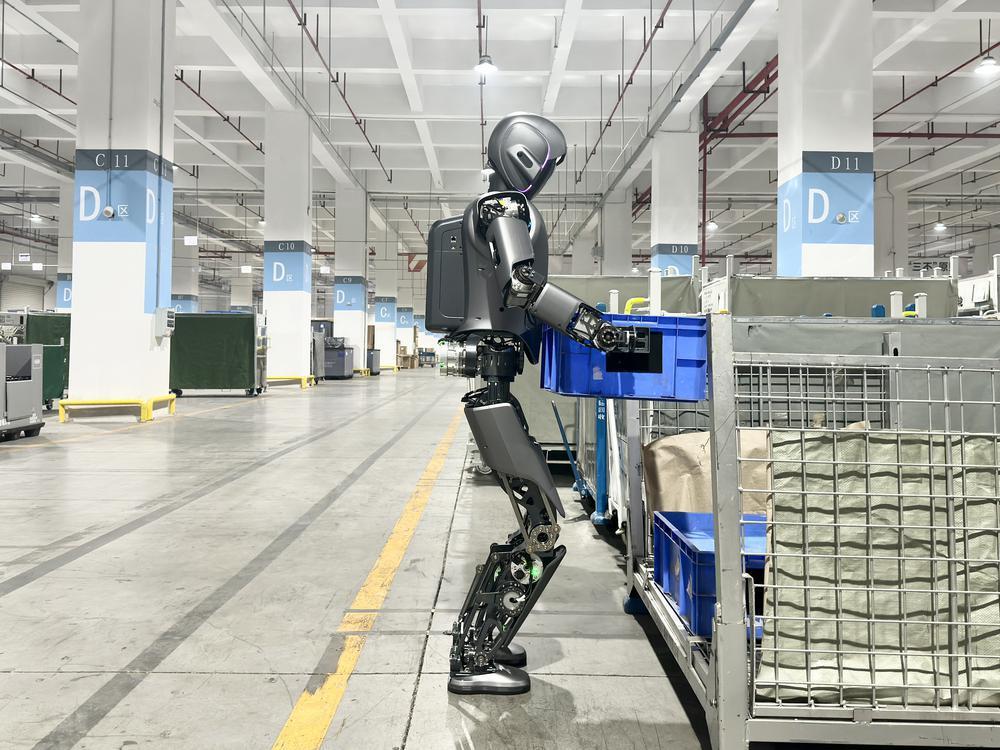

These achievements are the result of Guangdong's forward-thinking industrial layout and ongoing technological breakthroughs. As early as 2020, the province mapped out a development road map for its intelligent robotics industry cluster, centered around the two major cities, Guangzhou and Shenzhen, while promoting synergistic development in Zhuhai, Foshan, Dongguan, and Zhongshan. The goal is to achieve an operational revenue of 80 billion yuan for the intelligent robotics industry by 2025, establishing a leading hub for robotics innovation and production, which is recognized in China and abroad.
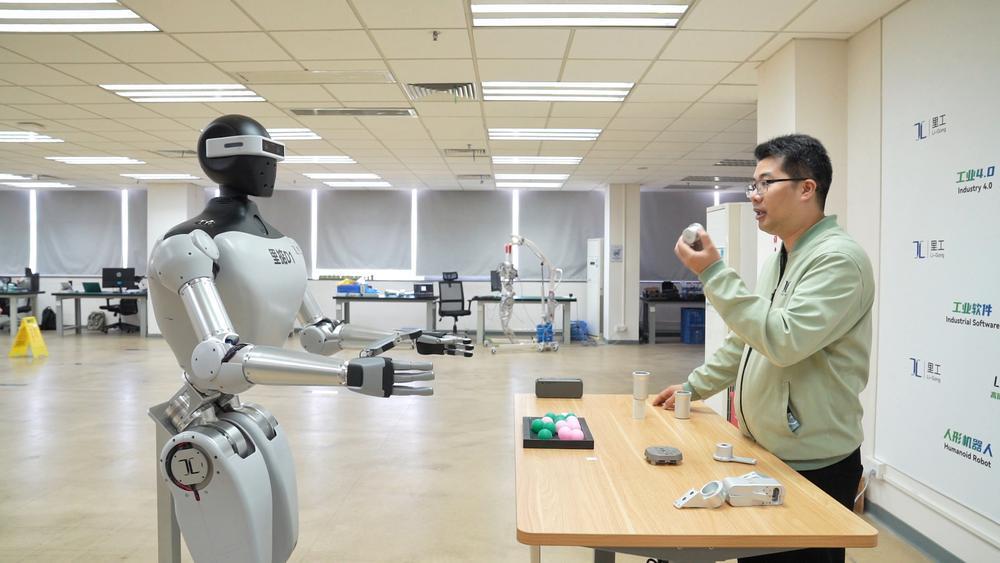

The value of artificial intelligence and robotics technology lies not only in their intrinsic capabilities but also in their profound impact on industrial transformation. Industrial robots are driving upgrades in traditional sectors such as construction, home appliances, ceramics, and automotive industries, while also accelerating the adoption of these technologies in emerging fields like transportation and logistics, autonomous driving, and smart agriculture. This transformation acts as a powerful "booster," reinforcing and optimizing traditional competitive advantages while cultivating and expanding emerging future industries, thereby fostering a deeper integration and collaborative development across the primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors.
Source: Lingnan on the Cloud
广东抢占机器人产业制高点
机器人特别是人形机器人的开发应用,关系到社会分工的新形态和人机协作的新内容,已成为科技竞争的新高地、未来产业的新赛道。广东省在刚刚召开的全省高质量发展大会上明确提出,要在人工智能和机器人领域集中发力,打造高技术、高成长、大体量的产业新支柱。
去年,广东工业机器人产量超24万台(套),占全国总量44%,连续五年位居全国第一并组建广东省具身智能机器人创新中心、广东省机器人创新中心等。既能引来库卡、大族、明珞、大疆、优必选等国内外知名企业,也能培育出一批走专精特新之路的本土“新秀”。
这一成果离不开广东前瞻性的产业布局与持续的技术攻关。早在2020年,广东便制定智能机器人产业集群发展路线图,围绕广州、深圳两大核心城市,带动珠海、佛山、东莞、中山等地协同发展。目标是到2025年,实现智能机器人产业营业收入800亿元,建成国内领先、世界知名的机器人产业创新和生产基地。
人工智能与机器人技术的价值不仅在于本身,更在于对产业变革的深远影响。工业机器人正推动建筑、家电、陶瓷、汽车等传统产业升级,同时在运输物流、无人驾驶、智慧农业等新兴领域加速落地。这一变革如同强劲“助推器”,既巩固优化传统优势产业,也培育壮大新兴未来产业,促进三次产业深度融合、协同发展。
文|李妹妍
图|羊城派资料图
译|洪婷
英文审校|赵凡
-
'Ne Zha 2' debuts in North America a sold-out Hollywood premiere
2025-02-10 20:13:09 -
People mourn the passing of Huang Xuhua, the chief designer of China's first-generation nuclear submarines
2025-02-10 20:13:14 -
The main anchorages of Shiziyang grand bridge in the GBA begin to take shape
2025-02-09 22:56:26 -
Original dance drama "Yingge" launches 2025 national tour, boosting Lingnan culture
2025-02-09 22:56:30