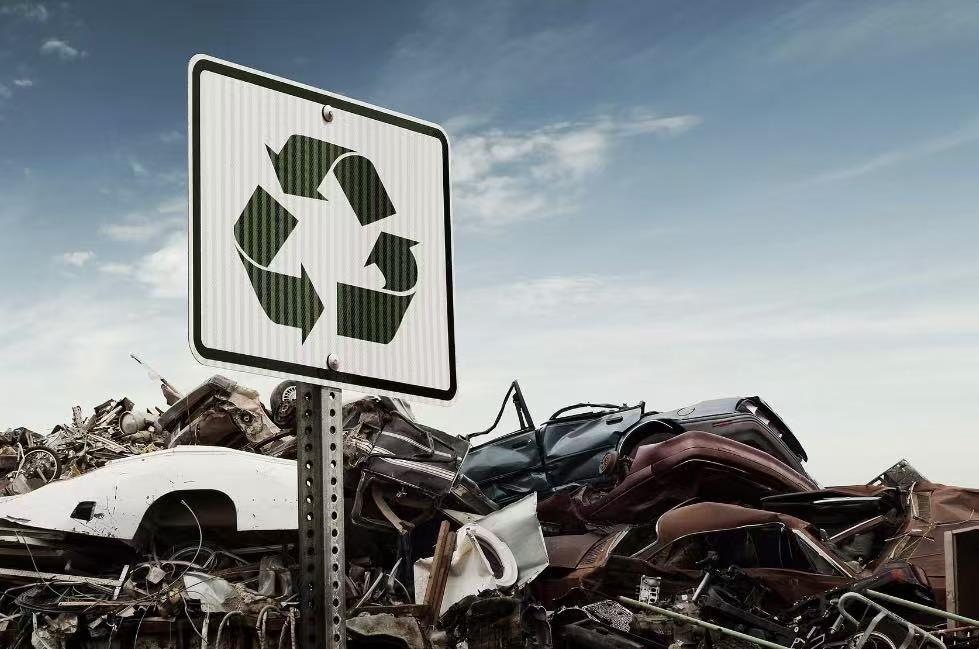
On October 18th, a new central enterprise, China Resources Recycling Group Co., Ltd., was established in Tianjin. Shareholders of the Group include several major central enterprises, such as Sinopec, China Minmetals, and China Resources Group. After its establishment, the Group will expand its recycling business to include scrapped vehicles, home appliances, and electronic products, as well as retired wind and photovoltaic equipment. This marks a significant step forward for China in its journey towards green and low-carbon circular development.
The Group focuses on the recycling and utilization of scrap steel, used batteries, waste plastics, and non-ferrous metals, with an expected annual utilization of scrap steel reaching 260 million tons. For instance, regarding waste plastic recycling, it is estimated that approximately 43 million tons of waste plastics will be incinerated or landfilled in China in 2023. If 50% of this waste can be converted through chemical recycling, it would be equivalent to developing an oil field with a capacity of over 60 million tons. This would play a crucial role in ensuring China's energy security and reducing resource waste.
Additionally, the Group will promote the establishment of a recycling network for discarded products and equipment, supporting companies in creating reverse logistics systems for used products. This effort will particularly focus on the efficient utilization of retired wind, solar equipment and batteries, aiming to advance green and low-carbon development. According to a report from the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), it is expected that by 2030, the global recycling rate for retired wind equipment could exceed 90%, generating an economic value of approximately 40 billion USD annually. These discarded products contain a wealth of recyclable resources, including steel, non-ferrous metals, precious metals, plastics, and rubber. Effectively recycling is akin to opening a "second mine", which can reduce the demand for raw materials and lessen the environmental impact of mineral resource extraction.
Source: Lingnan on the Cloud
中国成立新央企,聚焦资源循环利用引领绿色转型
10月18日,一家新的中央企业——中国资源循环集团有限公司在天津正式挂牌成立。中国资源循环集团股东成员包括中国石化、中国五矿、华润集团等多家中央企业。成立后,集团还将拓展报废机动车、家电及电子产品等相关耐用消费品和退役风电、光伏组件等重大装备产品的回收业务,标志着我国在绿色低碳循环发展道路上又迈出了坚实一步。
中国资源循环集团专注于废钢铁、废旧动力电池、废塑料和废有色金属的回收利用,预计每年废钢铁的利用量将达到2.6亿吨。以废塑料回收利用为例,据测算,2023年我国约4300万吨废塑料被焚烧或填埋,如果其中50%能够实现化学循环,就相当于开发了一个超过6000万吨的油田,对保障中国的能源安全,减少资源浪费具有重要意义。
此外,集团还将推动完善废旧产品设备回收网络,支持企业建立废旧产品的逆向物流体系,特别是在退役风电、光伏设备和动力电池的高效利用方面,致力于推动绿色低碳发展。根据国际可再生能源机构(IRENA)的报告,预计到2030年,全球退役风电设备的回收率可以达到90%以上,这将带来每年约400亿美元的经济价值。这些废旧产品设备中蕴藏着大量可循环利用的钢铁、有色金属、贵金属、塑料、橡胶等资源。对这些资源进行有效回收循环利用,相当于开启“第二矿山”,可以降低对原生资源的需求,减轻矿产资源开采对自然环境的压力。
文 | 国资小新、央视新闻
译 | 林佳岱
审 | 赵凡
-
International students at the Canton Fair: impressed by Chinese products and exchanging WeChat with global traders
2024-10-18 22:11:29 -
Poster丨Amazing! People from all over China enjoy the supermoon together
2024-10-18 21:02:40 -
Video|Industrial designs impress overseas merchants as domestic robot dog debuts at Canton Fair
2024-10-18 21:32:08 -
Beauty at the Canton Fair: The 'warmth' of Chinese intelligent manufacturing
2024-10-18 21:31:46