On September 29th, the Department of Culture and Tourism of Guangdong Province announced the official release of the long-awaited "Guangdong Provincial Cultural Heritage Protection Spatial Plan (2021-2035)" (hereinafter referred to as the Plan).
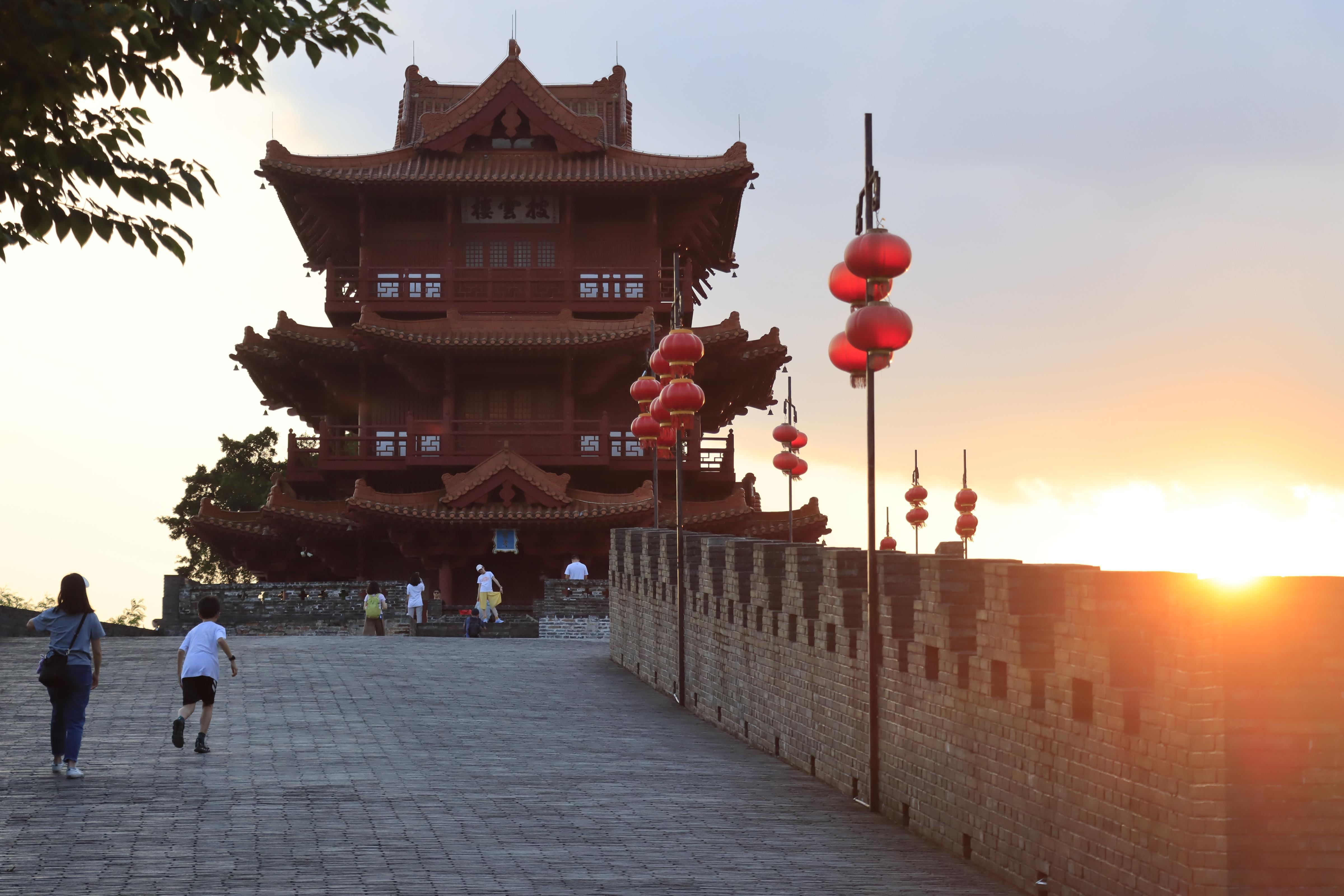

As a center of Lingnan culture, the birthplace of the Maritime Silk Road, and a key site of China's modern democratic revolution and reform and opening-up policy, Guangdong boasts a rich array of cultural relics and heritage from various historical periods, characterized by distinct contemporary and regional features. Currently, there are 131 major historical and cultural heritage sites protected at the national level, 887 heritage sites under Guangdong provincial-level protection, and over 5,000 heritage sites protected at the municipal or county level.
This Plan focuses on officially recognized historical and cultural heritage units, immovable relics yet to be recognized, as well as World Heritage Sites, areas with buried relics, and underwater cultural heritage protection areas. It prioritizes planning for national key cultural heritage sites, provincial sites, and the aforementioned buried and underwater areas.
By 2025, the Plan aims to fully incorporate the delineation of World Heritage Sites, 131 historical and cultural heritage sites protected at the national level, and 887 heritage sites under provincial-level protection in Guangdong province into a comprehensive spatial planning supervision system for Guangdong.
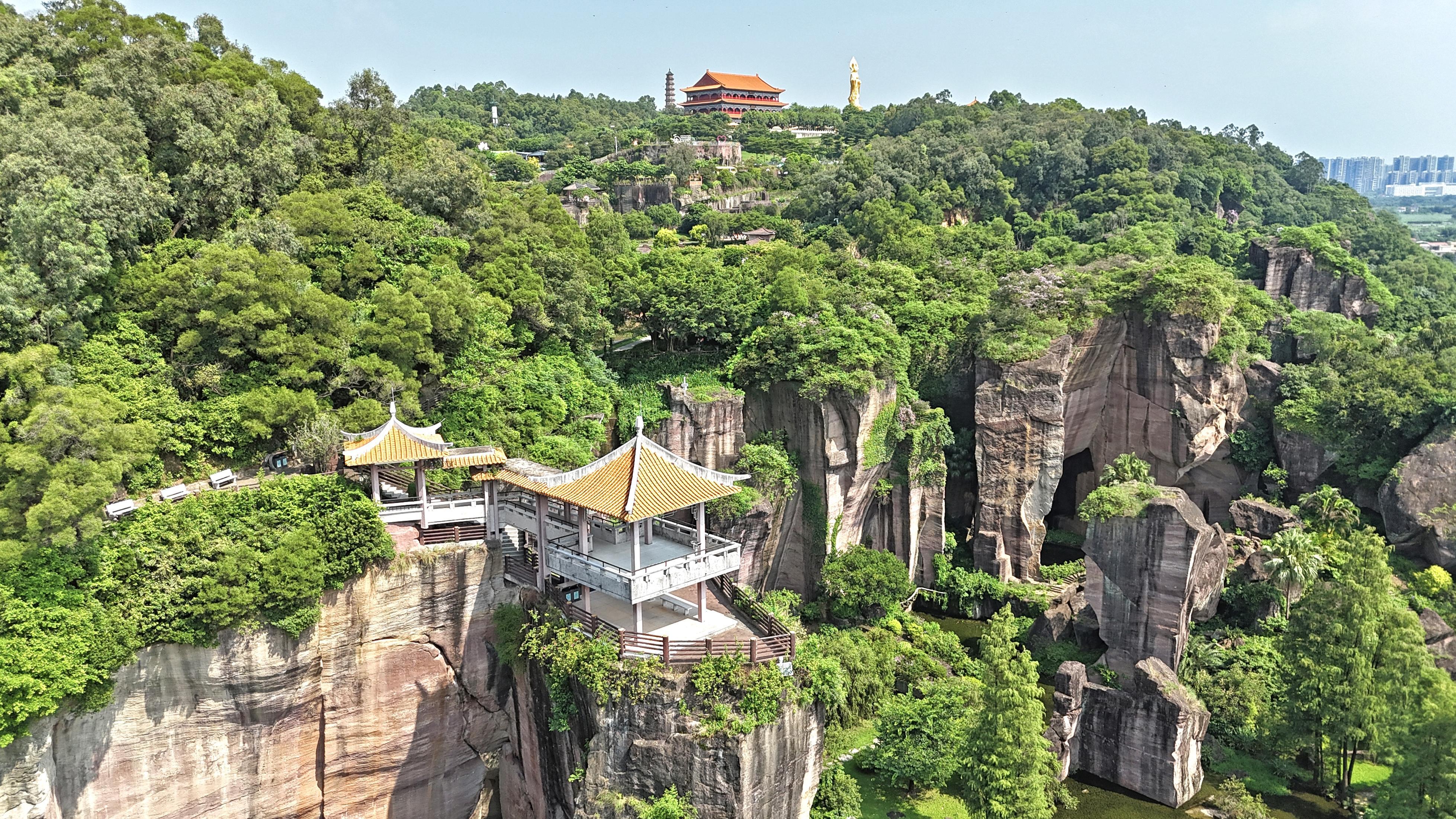

The Plan proposes a heritage utilization framework of "four corridors, three belts, and ten multi-point areas ", which aims to enhance thematic activation and regional integration, while outlining resource allocation requirements.
Focusing on the spatial characteristics of "historical transportation corridors and natural ecological corridors", the Plan includes the comprehensive development of four historical and cultural corridors: the Beijiang-Yuebei Ancient Road , the Dongjiang-Hanjiang Corridor , the Xijiang River Guangfu Corridor, and the Zhaolei Ancient Road .
Leveraging World Heritage applications, innovative protection of major sites, and the construction of the Long March National Cultural Park (Guangdong section), the Plan aims to establish three historical and cultural belts: the Maritime Silk Road heritage site (Guangdong), the Ming and Qing Dynasties' coastal defense heritage site (Guangdong), and the Long March heritage site, strengthening the integration of historical and cultural resources and tourism resources in these areas.
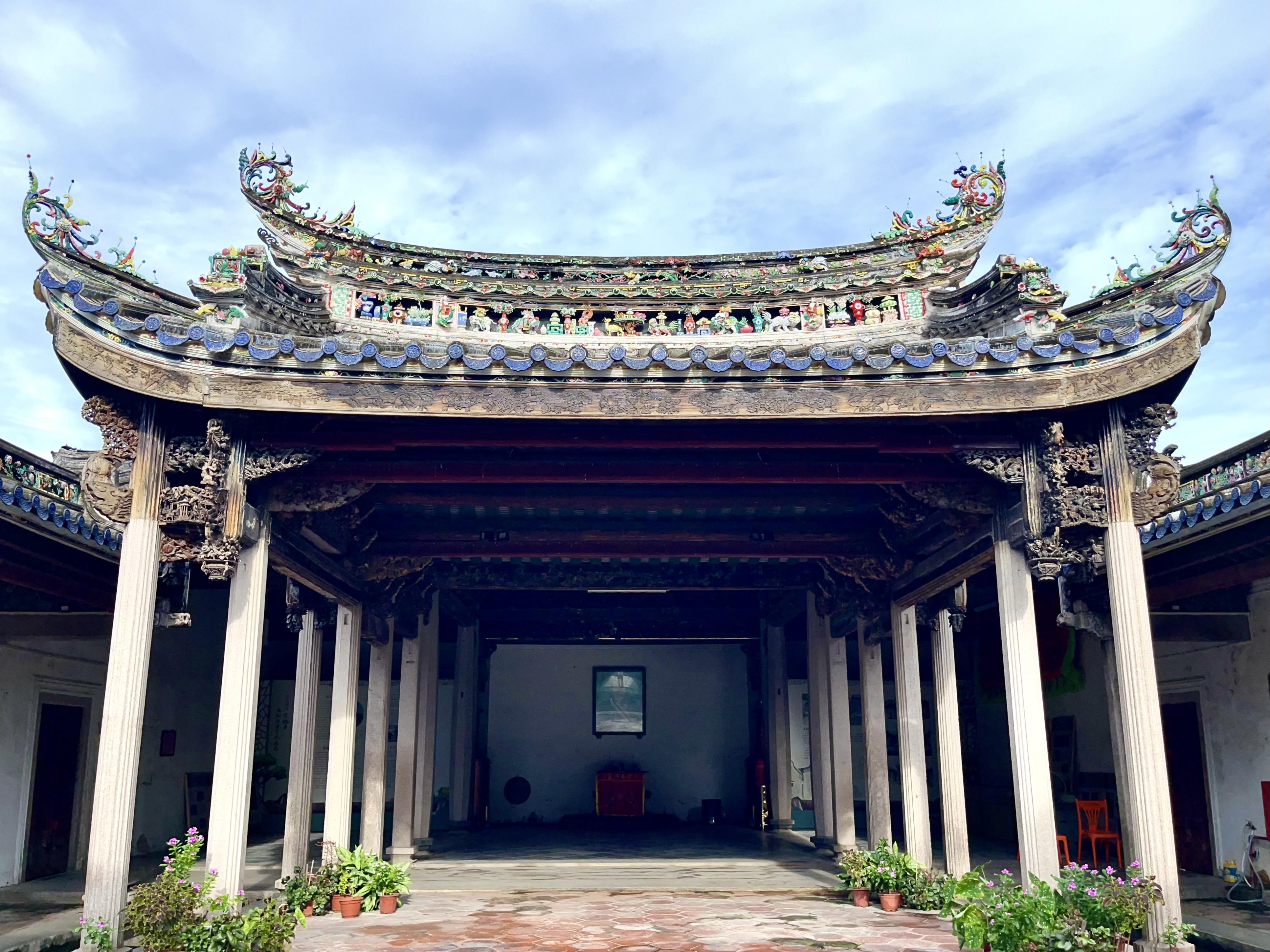

Furthermore, the Plan emphasizes regions and towns with high cultural resource evaluations, aiming to create ten historical and cultural areas-such as Guangzhou-Foshan-Zhaoqing, Shaoguan, Shenzhen-Dongguan-Huizhou, Jiangmen, Leizhou, Meizhou, Lianzhou-Liannan, Zhongshan-Zhuhai, Chaoshan, and Luoding-Yunan-to promote the systematic integration of thematic and cross-regional historical and cultural resources, thereby shaping regional cultural brands.
Source :Lingnan on the Cloud
重磅!《广东省文物保护空间规划》正式出台
9月29日,羊城晚报记者从广东省文化和旅游厅获悉,酝酿已久的《广东省文物保护空间规划(2021—2035)》(简称“规划”)已于近日正式出台。
作为岭南文化中心地、海上丝绸之路发祥地、中国近代民主革命策源地、改革开放前沿地,广东各历史时期保存下来的文物及文化遗产较为丰厚,具有鲜明的时代特征与地域特色。目前认定公布全国重点文物保护单位131处,广东省文物保护单位887处,市县级文物保护单位5000余处。
此规划将以全省核定公布的各级文物保护单位和尚未核定公布为文物保护单位的不可移动文物以及世界文化遗产、地下文物埋藏区、水下文物保护区等研究对象。其中,全国重点文物保护单位、省级文物保护单位以及地下文物埋藏区、水下文物保护区为重点规划对象。
规划明确,至2025年,广东省范围内世界文化遗产、131处全国重点文物保护单位、887处省级文物保护单位保护范围及建设控制地带、地下文物埋藏区及水下文物保护区的划定成果将100%纳入国土空间规划“一张图”实施监督信息系统。
规划还基于广东文物资源禀赋特点、历史文化价值及空间分布特征,提出“四廊三带、十片多点”的传承利用格局,强化主题性活化利用与区域整合,提出相关资源配置要求。
围绕“历史交通廊道+自然生态廊道”空间特征,提出深化北江—粤北古道历史文化廊道、东江—韩江历史文化廊道、西江广府历史文化廊道、肇雷古道历史文化廊道等4条历史文化廊道综合建设。
依托世界文化遗产申报、大遗址保护利用创新和长征国家文化公园(广东段)建设,打造海上丝绸之路史迹(广东)、明清海防遗产(广东)和长征史迹(广东)3条历史文化带,加强区域内文物文旅资源融合。
此外,规划还将以文物资源评价较高的区县及乡镇为重点区域,打造广佛肇、韶关、深莞惠、江门、雷州、梅州、连州—连南、中山—珠海、潮汕、罗定—郁南等10个历史文化片区,推进主题性、跨区域性的各类历史文化资源系统整合,塑造地域文化品牌。
文|记者 文艺 通讯员 粤文旅宣
译|赵凡
英文审校|林佳岱
-
The only in Guangdong: Nan'ao round-the-island road in Shantou selected as one of the most beautiful self-driving routes
2024-09-30 22:19:19 -
Poster丨What kind of experience is it to spend the National Day holiday in the Overseas Chinese Ancient Town?
2024-09-30 21:35:59 -
Video + Photos|The Guangzhou Central Axis celebrates the National Day with a grand performance
2024-09-30 19:55:50 -
Video | Lin Youyi's decade: From curiosity to reluctance to leave | Love Cross The Strait①
2024-09-30 18:44:34