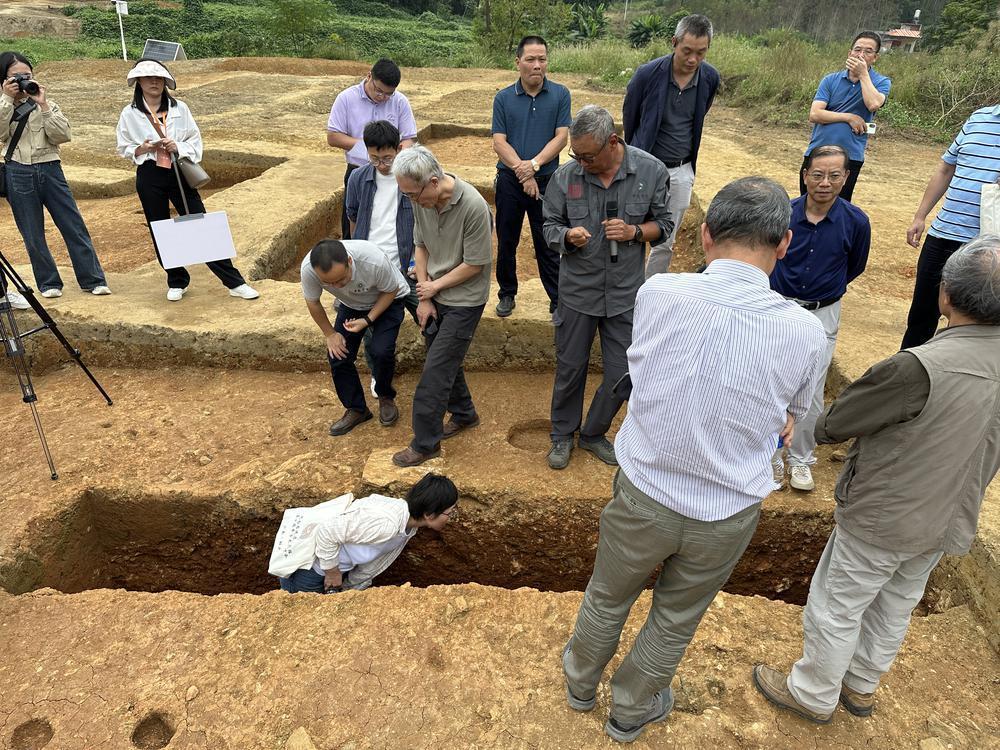
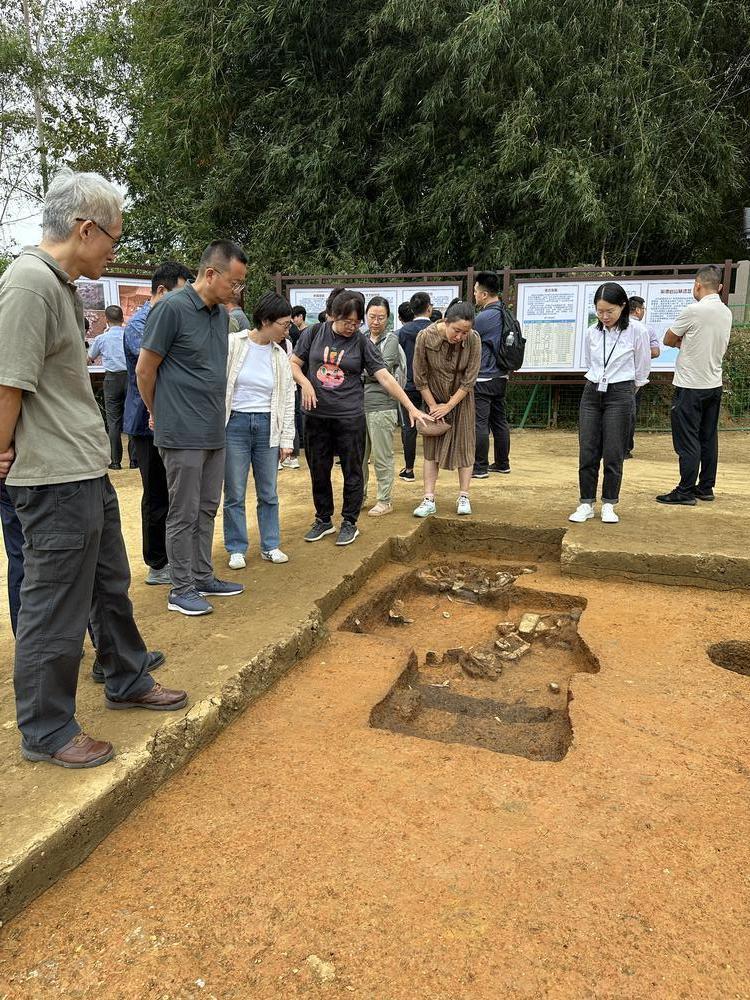
In recent days, the northern region of Guangdong welcomed nearly a hundred archaeology experts, scholars, and young academics from across the country. They gathered to commemorate the 50th anniversary of the excavation of the Shixia Site, contributing their wisdom and expertise to Guangdong's pre-Qin archaeology and the "Early Origins of Lingnan Project."
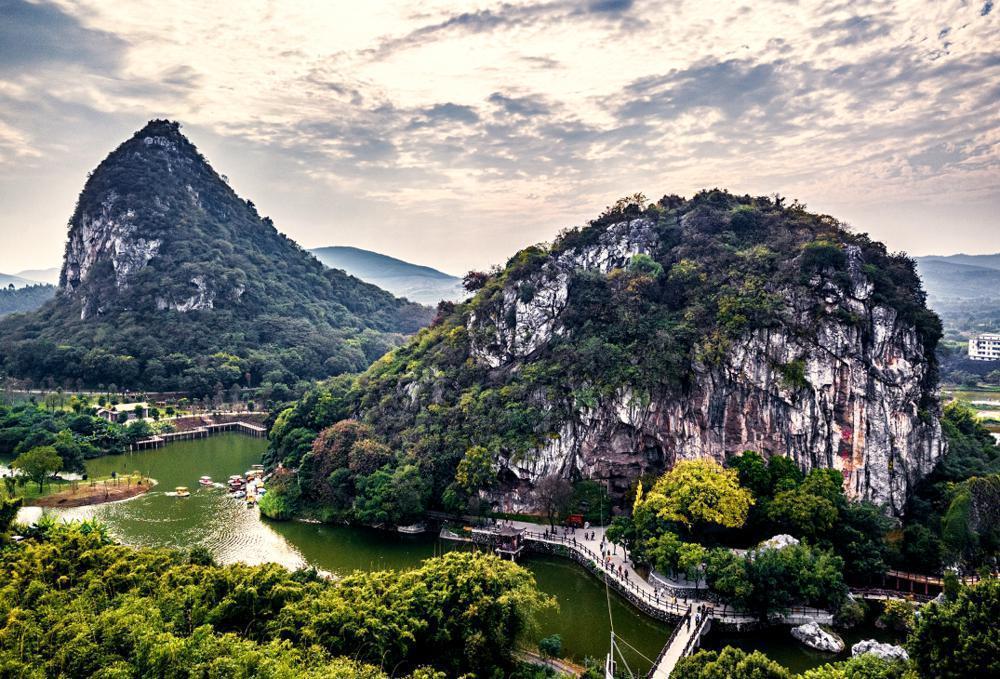

On October 13th, reporters from the Yangcheng Evening News accompanied the experts on a journey to explore and investigate the Shixia Site in Qujiang, the Yanshanzhai Site in Yingde, and the Qingtang Site in Yingde. Through on-site visits, they delved into the pre-Qin archaeology in Guangdong and sought the footprints of Lingnan ancestors.
Commemorating the 50th anniversary of Shixia Site excavation
The Shixia Site is one of the most significant pre-Qin archaeological discoveries in Guangdong to date. It is considered one of the top 100 major archaeological findings in 20th-century China. The site was excavated three times from the end of 1973 to the end of 1978, revealing an area of 3,666 square meters and 132 graves.
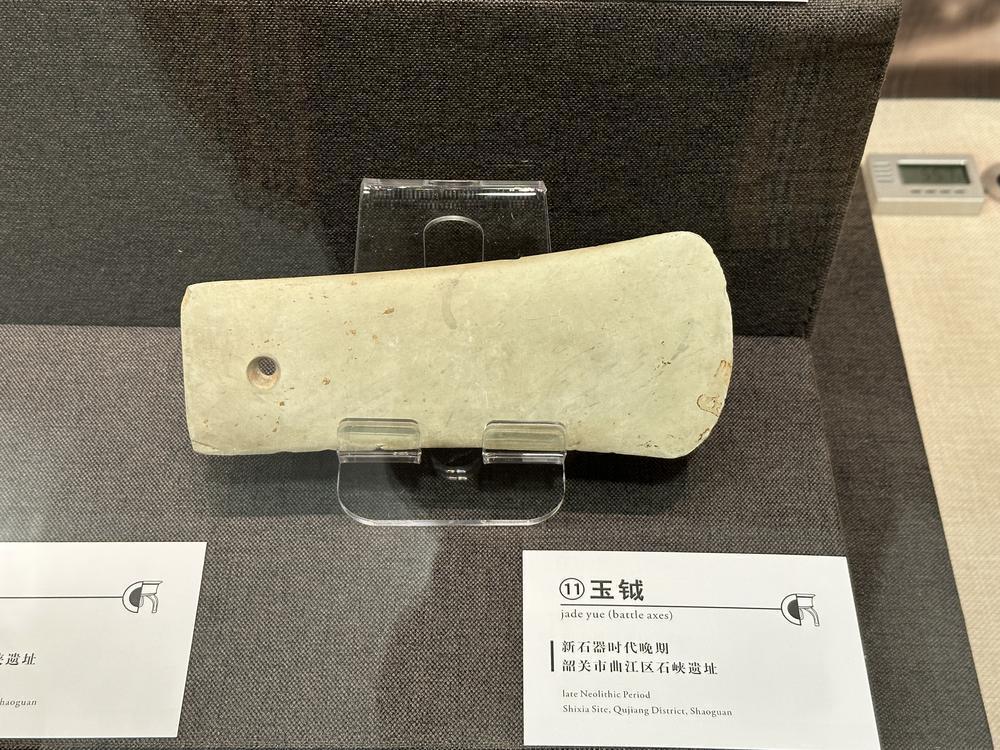
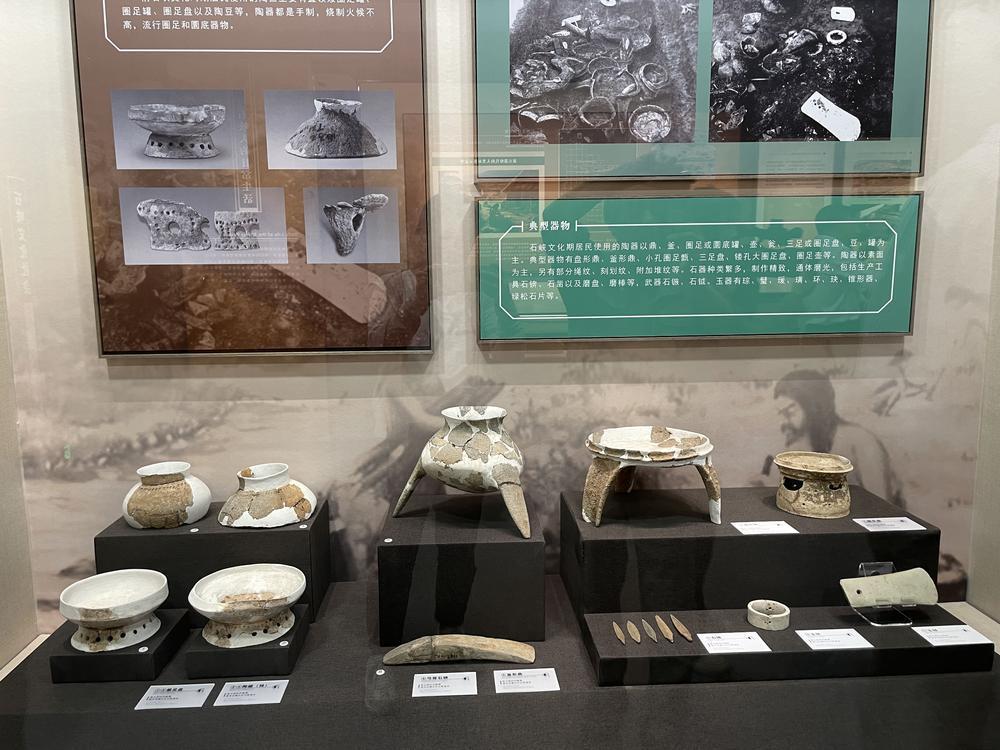


Research indicates that the Shixia Culture dates from 5,000 to 4,000 years ago, a period when residents began to move out of caves and settle on relatively plateaus.
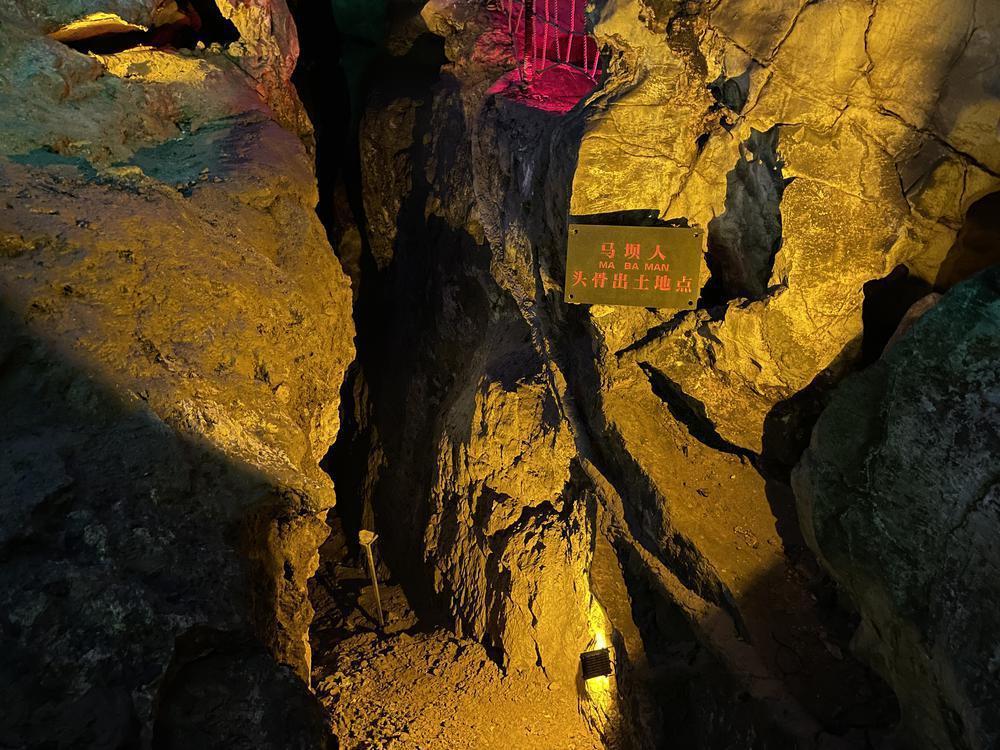


They constructed houses with wooden bones and mud walls as well as practiced rebury customs. Their artifacts included polished stone tools and pottery adorned with simple patterns for cooking. They performed various daily activities such as fishing, hunting, farming, weaving linen, and sewing clothing.
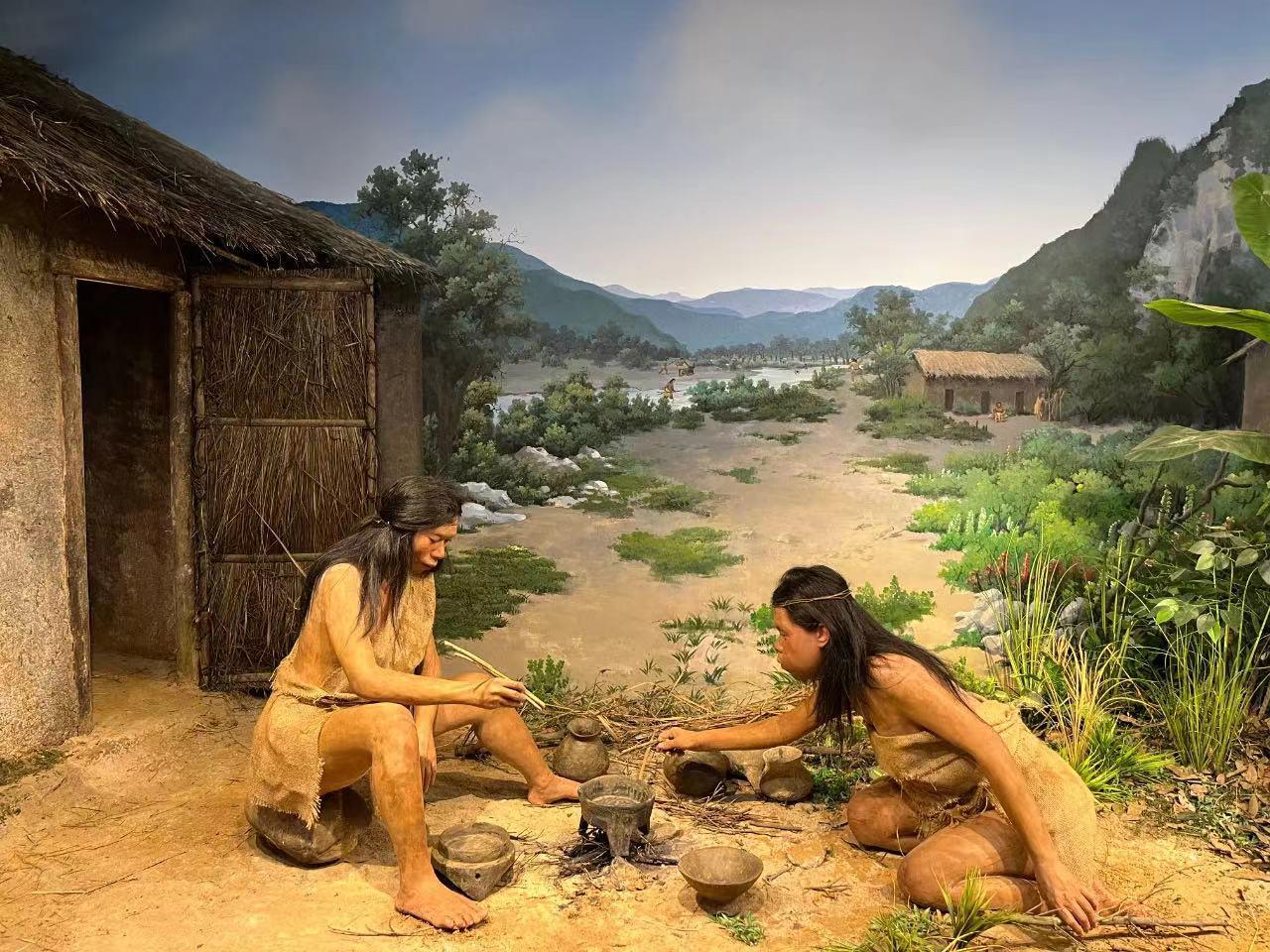

The discovery and excavation of the Shixia Site hold exceptional significance in Guangdong's archaeological history. It is a crucial step in exploring the relationship between Lingnan culture and related cultures, as well as the starting point for investigating the interactions of our ancient ancestors with people in Southeast Asia.
Yanshanzhai Site:the best commemoration of the Shixia Site's 50th anniversary
The Shixia Culture represents a cultural highpoint in the Late Neolithic period of Lingnan, with its primary influence area being the northern region of Guangdong. The Yanshanzhai Site is a vital settlement site for the Shixia Culture.
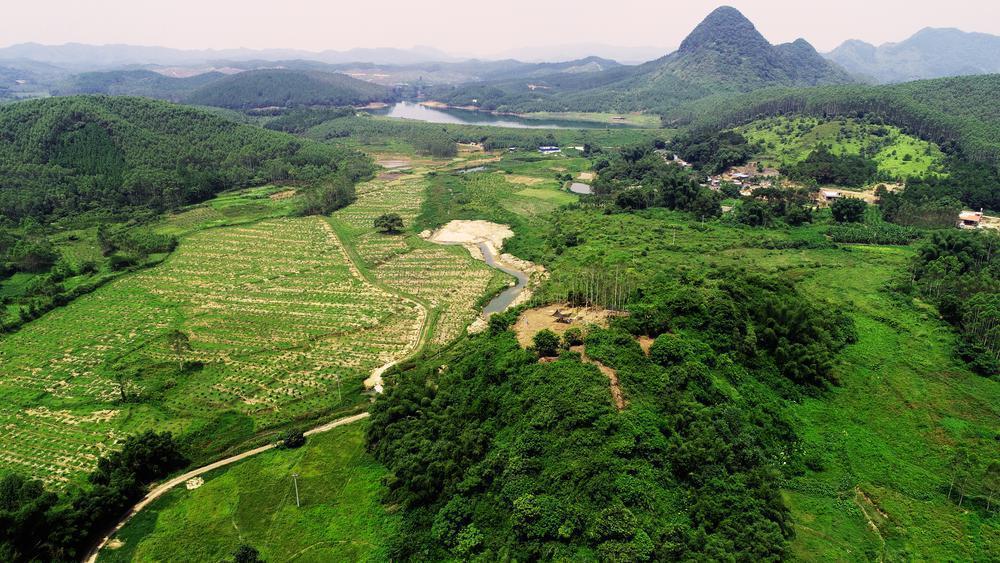

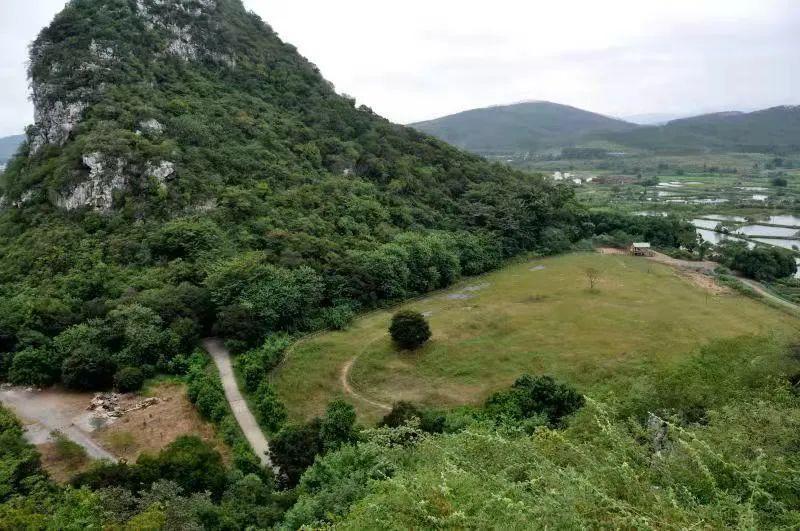
The Yanshanzhai Site is also the largest known settlement site from the Late Neolithic to the Xia-Shang period in Lingnan to date.
Covering an area of approximately 100,000 square meters, it includes multiple functional divisions such as residential areas and burial zones. It is currently the only large pre-Qin settlement site in Guangdong located on a limestone peak, with rich remains found in multiple caves and peripheral plateaus.
Yan Wenming, a senior professor at Peking University, stated, "Fifty years ago, the discovery of the Shixia Site became a significant breakthrough in Guangdong's archaeological history, filling the gap in the archaeology of the New Stone Age in Guangdong. The discovery of the Yanshanzhai Site is the best way to commemorate the 50th anniversary of the Shixia Site's excavation."
Qingtang Archaeological Site Park planning underway
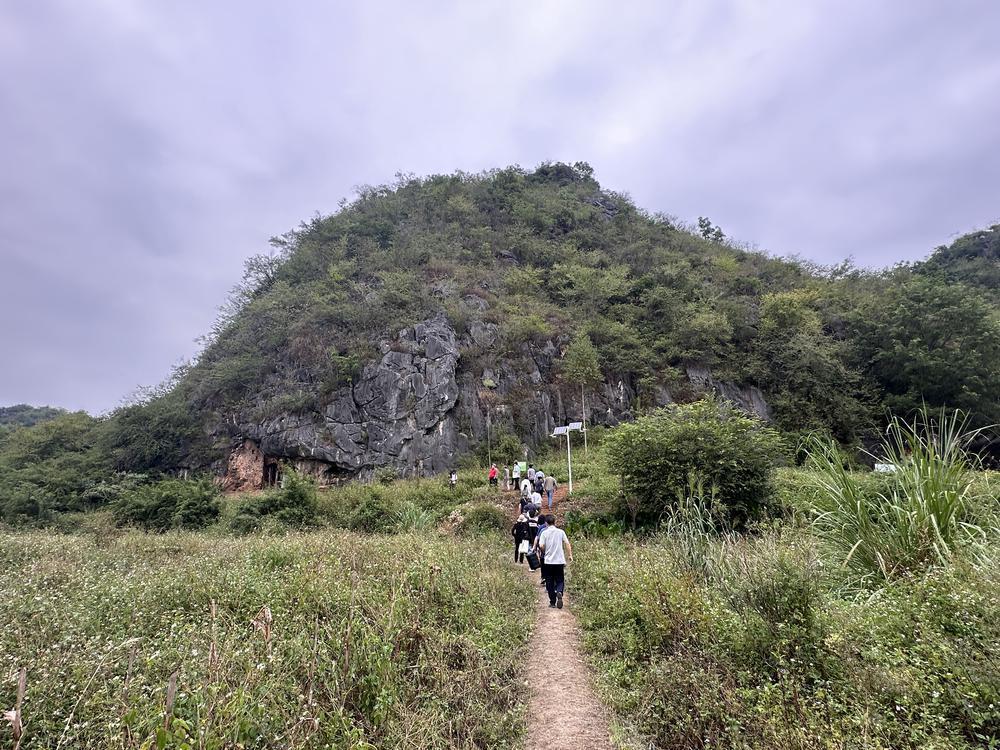

Later, experts visited the Qingtang Site, located less than a kilometer away from the Yanshanzhai Site. This site represents a typical cave site from the transitional period between the Old and New Stone Ages in South China.
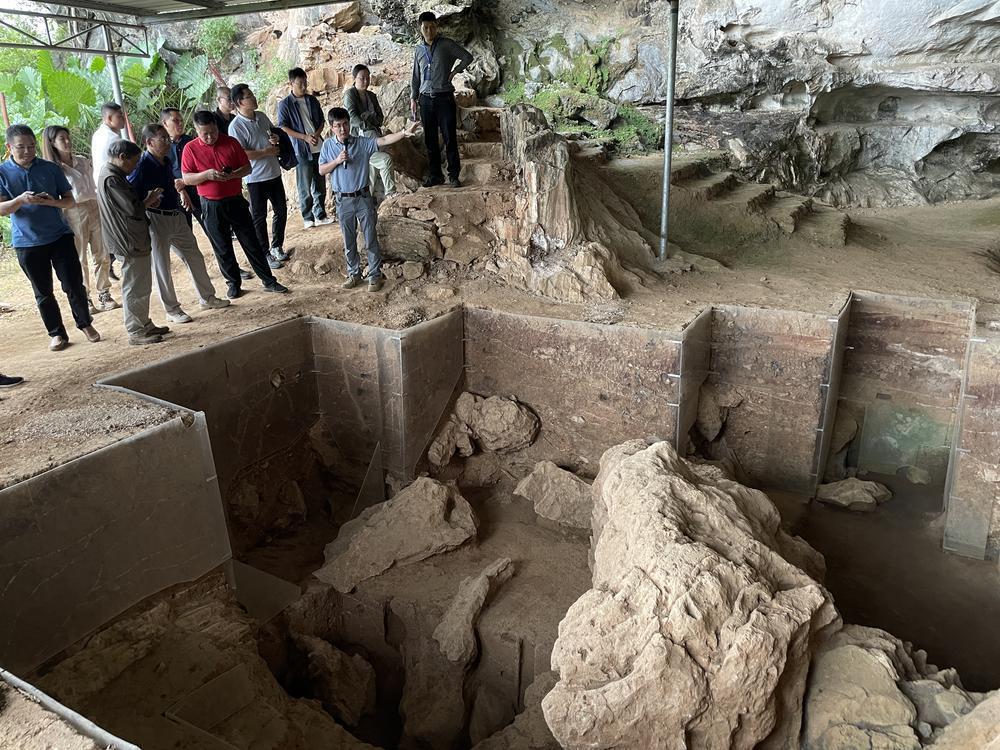

From 2016 to 2018, archaeological excavations at the Qingtang Site revealed the earliest confirmed burial practices in South China, dating back 13,500 years. Experts unearthed the most complete human fossils from approximately 10,000 years ago within Guangdong's borders. Moreover, they discovered the oldest perforated clamshells in South China and early pottery from Guangdong.
In December 2022, the Yingde Qingtang Archaeological Site Park was included in the fourth batch of national archaeological site park projects.
近百位考古专家齐聚韶关,探寻岭南远古先民的足迹
近日,粤北第一次迎来了近百位来自全国各地的考古学专家、学者和青年学人,共同纪念石峡遗址发掘五十周年,也为广东史前先秦考古以及“早期岭南探源工程”贡献智慧与力量。

10月13日,羊城晚报记者跟随专家学者一行前往曲江石峡遗址、英德岩山寨遗址、英德青塘遗址参观考察,从韶关曲江到清远英德,在实地探访中感受广东先秦考古的世纪历程,探寻岭南远古先民的足迹。
石峡遗址:广东先秦时期最为重要的遗址之一
石峡遗址是迄今发现的广东先秦时期最为重要的遗址之一,也是20世纪中国百项考古大发现。遗址于1973年底至1978年底经过三次发掘,揭露面积3666平方米,清理墓葬132座。

研究表明,石峡文化距今5000-4000年,这个时期的居民开始走出洞穴,选择在相对低缓的台地上定居生活。
他们以木骨泥墙建造房屋,以二次葬习俗埋葬死者。他们制造出通体磨光的石器,煮饭的陶器上装饰着朴素的花纹,日常劳作或渔猎采集,或种植稻米,还会纺织麻布,缝制衣裳。
石峡遗址的发现和发掘对于广东考古学史意义非凡,是探索岭南与相关文化关系的一个重要环节,是探索我国古代先民与东南亚地区交往的一个出发点。
岩山寨遗址:岭南迄今发现规模最大的新石器时代至夏商时期中心聚落遗址
石峡文化代表了岭南新石器晚期时间段的文化高地,它的主要传播和影响地区为粤北地区,岩山寨遗址就是一处重要的石峡文化聚落遗址。

同时,岩山寨遗址也是岭南迄今发现规模最大的新石器时代至夏商时期中心聚落遗址。
岩山寨遗址面积约10万平方米,包含居住区、墓葬区等多个功能分区。它是目前广东唯一在石灰岩孤峰顶部、山体多个溶洞和外围台地均发现丰富遗存的大型先秦聚落遗址。

北京大学资深教授严文明先生表示:五十年前,石峡遗址成为广东考古史上的重大突破,填补了广东新石器时代考古的空白,“英德岩山寨遗址的发现,就是对石峡遗址发掘五十周年的最好纪念。”
青塘考古遗址:年代最早的可确认葬式的墓葬
随后,专家们到距离岩山寨遗址不到一公里的青塘遗址进行考察,它是华南地区新旧石器时代过渡阶段典型的洞穴遗址。
经过2016年至2018年的考古发掘,青塘遗址发现了距今1.35万年、华南地区年代最早的可确认葬式的墓葬,出土了广东境内保存最完整的距今1万年前的古人类化石,并发现了目前华南最早的穿孔蚌器和广东最早的早期陶器。
2022年12月,英德青塘考古遗址公园成功入选第四批国家考古遗址公园立项名单。
文、图 | 记者 文艺 朱绍杰 梁善茵
译 | 刘佳慧
-
Y Talk㉛|China is a determined believer in opening-up封闭还是开放?中国坚定选择后者!
2023-10-15 15:55:03 -
Ecological construction in Shaoguan | Research trip for the 45th anniversary of reform and opening-up
2023-10-14 22:22:25 -
First batch of southbound migratory birds arrive in Guangdong, kicking off birdwatching season
2023-10-14 22:22:42 -
6th World Hakka Businessmen Convention to be held in Meizhou from November 2nd to 4th
2023-10-13 23:32:59